NEURON 1)5)
← Back
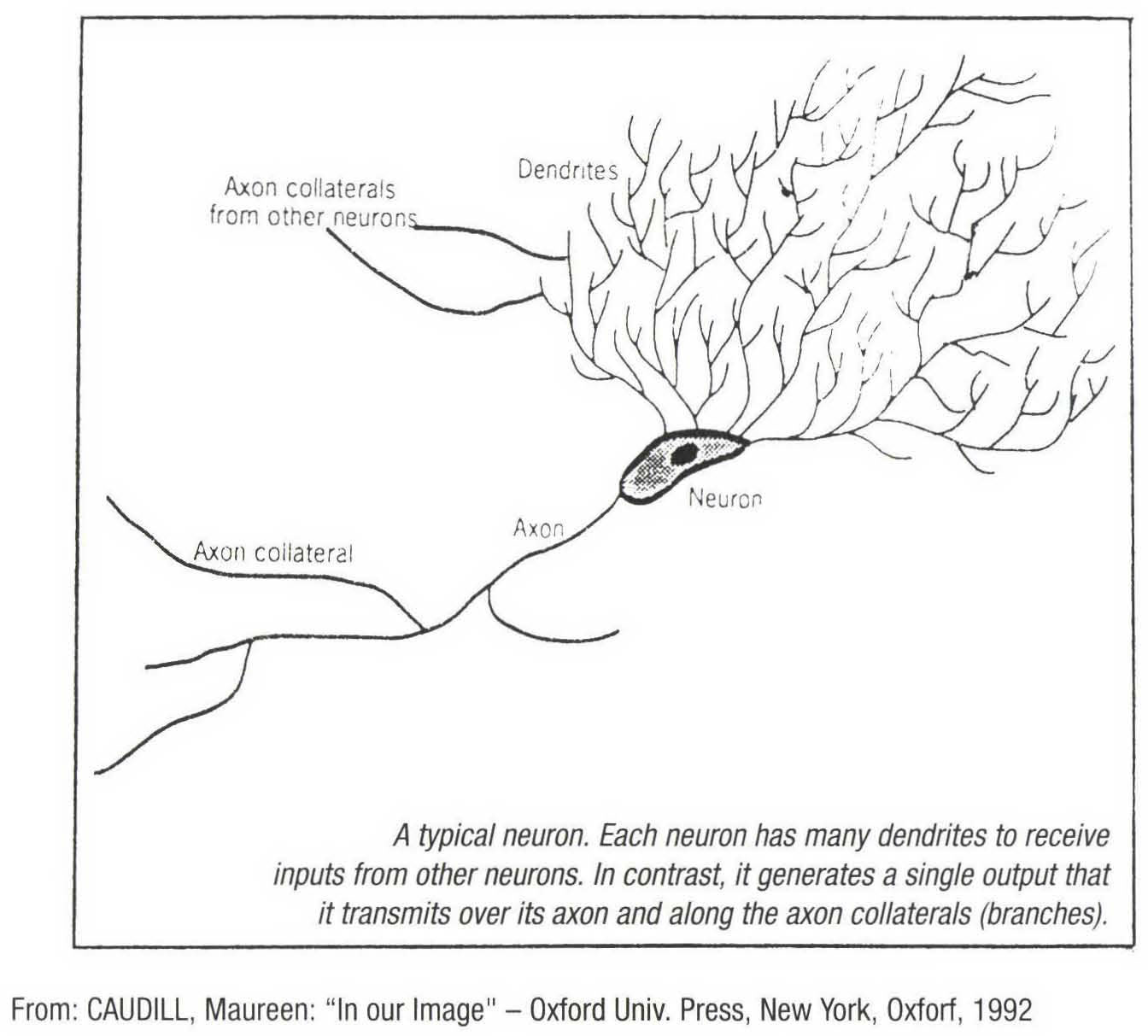
A cell of nerve tissue whose parts are a nucleus, afferent receptors and an efferent axon.
Neurons communicate with each others through intervals called synapses (where complex biochemical exchanges take place), and within very intricated networks, particularly in the neocortex, the most organized part of the human brain.
C. KOCH and G. LAURENT state: "Exquisite molecular machines endow neurons with complex nonlinear dynamical properties, regardless of the animal's size or evolutionary lineage. Moreover, these properties are not static, but adaptively tunable" (1999, p.97).
→ Brain; Brain circuit; Brain metaphor
Categories
- 1) General information
- 2) Methodology or model
- 3) Epistemology, ontology and semantics
- 4) Human sciences
- 5) Discipline oriented
Publisher
Bertalanffy Center for the Study of Systems Science(2020).
To cite this page, please use the following information:
Bertalanffy Center for the Study of Systems Science (2020). Title of the entry. In Charles François (Ed.), International Encyclopedia of Systems and Cybernetics (2). Retrieved from www.systemspedia.org/[full/url]
We thank the following partners for making the open access of this volume possible:

